Challenges to Electric Vehicle Adoption

Adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, driven by factors such as rising fuel costs, improvements in battery technology, the availability of more affordable options, and government incentives. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger generations, who are more environmentally conscious. While these developments are encouraging, the EV industry still faces several pressing challenges.
Improving Charging Infrastructure
According to a survey by BDEV, nearly 70% of EV drivers demand a broader network of charging stations in residential areas. The survey further highlights that 62% of EV drivers consider finding a suitable home charging solution to be a major concern, and 48% are apprehensive about potential issues related to charging in public spaces. These statistics underscore the urgency for the EV industry to address these charging infrastructure challenges.
With the European Union aiming for carbon neutrality by 2050 and a 55% reduction in emissions by 2030, and Germany specifically aiming to have 15 million electric cars and 1 million public charging points by 2030, the increasing adoption of electric vehicles calls for a rapid expansion of charging infrastructure.
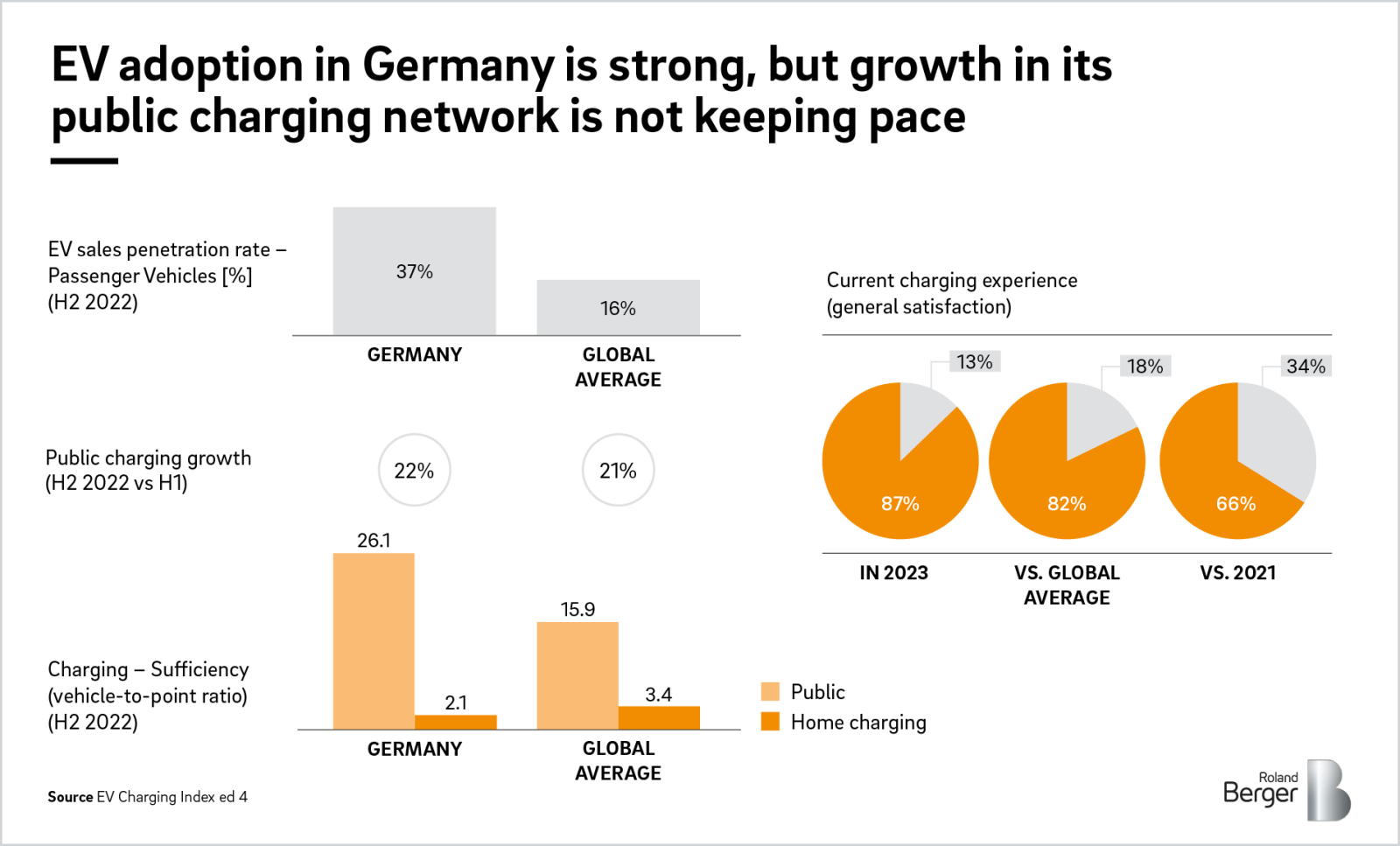
According to the EV Charging Index Edition 4 by Roland Berger, Germany maintains its position as a frontrunner in EV adoption, but it must accelerate the expansion of its public charging infrastructure.
Expanding Public Charging Infrastructure
According to the International Energy Agency's Global EV Outlook 2023, Europe's fast charger stock surpassed 70,000 by the end of 2022, a 55% increase from 2021. Germany leads with over 12,000 fast chargers, followed by France (9,700) and Norway (9,000).
To meet the demand for mass EV adoption, the EU-27 must expand its charging infrastructure significantly. McKinsey estimates that by 2030, the EU will need to increase its public charging stations from 340,000 to 3.4 million. This substantial growth requires a concerted effort from governments, industry players, and utility companies to accelerate infrastructure development.
Charging costs
KPMG points out that high purchase prices and increasing charging costs pose significant barriers to EV adoption in Europe. The complexity and diversity in charging pricing systems create challenges for both service providers and EV drivers. This pricing landscape also makes interoperability difficult, requiring extensive communication between service providers and operators to share pricing information.
The significant differences in tariffs among charging providers, often tied to long-term fixed rates, highlight the importance of price comparison for EV drivers. In response, various software applications and tools have emerged to help EV drivers find affordable public charging stations, promoting transparency.
Adapting to Charging Speeds
While the convenience and environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are widely recognised, charging speeds can pose a challenge for some drivers. Unlike gasoline-powered vehicles that can be refueled in a matter of minutes, EVs often require longer charging times, particularly when using standard Type 1 or Type 2 chargers. This can be a significant adjustment for drivers accustomed to the quick refueling process of conventional cars.
Weather Impact on Charging Performance
Extreme weather conditions, including intense heat, freezing cold, heavy rain, and harsh storms, can significantly impact the performance and longevity of EV charging cables, connectors, and the overall charging infrastructure. Public charging stations, often located outdoors and exposed to these elements, are particularly vulnerable to weather-related damage.
Ensuring Energy Supply for EV Charging
Meeting the energy needs of the growing electric vehicle (EV) industry is a major challenge. Utilities will need to expand their infrastructure to generate and efficiently distribute the required electricity to charging points. This is challenging due to aging electrical infrastructure, instances where peak demand exceeds supply, and the varying ability of different countries to implement electrification policies. Overcoming these power supply challenges is critical to the sustainable growth of EV adoption.
Conclusion
The transition from conventional gasoline-powered vehicles to electric-powered ones is picking up speed worldwide, driven by the pressing need for environmental sustainability and energy independence. However, this transition success rests on the establishment of a resilient infrastructure and a nurturing ecosystem that can accommodate the increasing EV population.
More developed markets such as China and several European countries have made significant strides in EV adoption, providing valuable lessons for other nations. These countries have successfully implemented incentive schemes, invested heavily in infrastructure development, and fostered a supportive regulatory environment. Their experiences can guide other countries as they embark on their own EV transition journeys.
📲 Follow us on Instagram and Facebook for more information and news about electric cars and sustainable mobility!